Android运行时ART加载OAT文件的过程
目录
一,概述
1.1 OAT是如何产生的
一,概述
OAT文件是一种Android私有ELF文件格式,它不仅包含有从DEX文件翻译而来的本地机器指令,还包含有原来的DEX文件内容。这使得我们无需重新编译原有的APK就可以让它正常地在ART里面运行,也就是我们不需要改变原来的APK编程接口
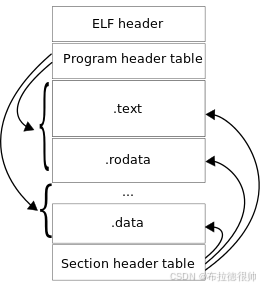
为了更好了弄明白oat文件的格式,目前还需要看下elf 文件格式
oat文件格式
作为Android私有的一种ELF文件,OAT文件包含有两个特殊的段oatdata和oatexec,前者包含有用来生成本地机器指令的dex文件内容,后者包含有生成的本地机器指令,它们之间的关系通过储存在oatdata段前面的oat头部描述。此外,在OAT文件的dynamic段,导出了三个符号oatdata、oatexec和oatlastword,它们的值就是用来界定oatdata段和oatexec段的起止位置的。其中,[oatdata, oatexec - 1]描述的是oatdata段的起止位置,而[oatexec, oatlastword + 3]描述的是oatexec的起止位置。要完全理解OAT的文件格式,除了要理解本文即将要分析的OAT加载过程之外,还需要掌握接下来文章分析的类和方法查找过程。
1.1 OAT是如何产生的
/Volumes/aosp/android-8.1.0_r52/frameworks/native/cmds/installd/dexopt.cpp
static void run_dex2oat(int zip_fd, int oat_fd, int input_vdex_fd, int output_vdex_fd, int image_fd,
const char* input_file_name, const char* output_file_name, int swap_fd,
const char* instruction_set, const char* compiler_filter,
bool debuggable, bool post_bootcomplete, int profile_fd, const char* class_loader_context) {
static const unsigned int MAX_INSTRUCTION_SET_LEN = 7;
if (strlen(instruction_set) >= MAX_INSTRUCTION_SET_LEN) {
ALOGE("Instruction set %s longer than max length of %d",
instruction_set, MAX_INSTRUCTION_SET_LEN);
return;
}
// Get the relative path to the input file.
const char* relative_input_file_name = get_location_from_path(input_file_name);
char dex2oat_Xms_flag[kPropertyValueMax];
bool have_dex2oat_Xms_flag = get_property("dalvik.vm.dex2oat-Xms", dex2oat_Xms_flag, NULL) > 0;
char dex2oat_Xmx_flag[kPropertyValueMax];
bool have_dex2oat_Xmx_flag = get_property("dalvik.vm.dex2oat-Xmx", dex2oat_Xmx_flag, NULL) > 0;
char dex2oat_threads_buf[kPropertyValueMax];
bool have_dex2oat_threads_flag = get_property(post_bootcomplete
? "dalvik.vm.dex2oat-threads"
: "dalvik.vm.boot-dex2oat-threads",
dex2oat_threads_buf,
NULL) > 0;
char dex2oat_threads_arg[kPropertyValueMax + 2];
if (have_dex2oat_threads_flag) {
sprintf(dex2oat_threads_arg, "-j%s", dex2oat_threads_buf);
}
char dex2oat_isa_features_key[kPropertyKeyMax];
sprintf(dex2oat_isa_features_key, "dalvik.vm.isa.%s.features", instruction_set);
char dex2oat_isa_features[kPropertyValueMax];
bool have_dex2oat_isa_features = get_property(dex2oat_isa_features_key,
dex2oat_isa_features, NULL) > 0;
char dex2oat_isa_variant_key[kPropertyKeyMax];
sprintf(dex2oat_isa_variant_key, "dalvik.vm.isa.%s.variant", instruction_set);
char dex2oat_isa_variant[kPropertyValueMax];
bool have_dex2oat_isa_variant = get_property(dex2oat_isa_variant_key,
dex2oat_isa_variant, NULL) > 0;
const char *dex2oat_norelocation = "-Xnorelocate";
bool have_dex2oat_relocation_skip_flag = false;
char dex2oat_flags[kPropertyValueMax];
int dex2oat_flags_count = get_property("dalvik.vm.dex2oat-flags",
dex2oat_flags, NULL) = 0) {
have_dex2oat_swap_fd = true;
sprintf(dex2oat_swap_fd, "--swap-fd=%d", swap_fd);
}
if (image_fd >= 0) {
have_dex2oat_image_fd = true;
sprintf(dex2oat_image_fd, "--app-image-fd=%d", image_fd);
}
if (have_dex2oat_Xms_flag) {
sprintf(dex2oat_Xms_arg, "-Xms%s", dex2oat_Xms_flag);
}
if (have_dex2oat_Xmx_flag) {
sprintf(dex2oat_Xmx_arg, "-Xmx%s", dex2oat_Xmx_flag);
}
// Compute compiler filter.
bool have_dex2oat_compiler_filter_flag = false;
if (skip_compilation) {
strcpy(dex2oat_compiler_filter_arg, "--compiler-filter=extract");
have_dex2oat_compiler_filter_flag = true;
have_dex2oat_relocation_skip_flag = true;
} else if (compiler_filter != nullptr) {
if (strlen(compiler_filter) + strlen("--compiler-filter=") 0;
if (have_dex2oat_compiler_filter_flag) {
sprintf(dex2oat_compiler_filter_arg,
"--compiler-filter=%s",
dex2oat_compiler_filter_flag);
}
}
// Check whether all apps should be compiled debuggable.
if (!debuggable) {
char prop_buf[kPropertyValueMax];
debuggable =
(get_property("dalvik.vm.always_debuggable", prop_buf, "0") > 0) &&
(prop_buf[0] == '1');
}
char profile_arg[strlen("--profile-file-fd=") + MAX_INT_LEN];
if (profile_fd != -1) {
sprintf(profile_arg, "--profile-file-fd=%d", profile_fd);
}
// Get the directory of the apk to pass as a base classpath directory.
char base_dir[arraysize("--classpath-dir=") + PKG_PATH_MAX];
std::string apk_dir(input_file_name);
unsigned long dir_index = apk_dir.rfind('/');
bool has_base_dir = dir_index != std::string::npos;
if (has_base_dir) {
apk_dir = apk_dir.substr(0, dir_index);
sprintf(base_dir, "--classpath-dir=%s", apk_dir.c_str());
}
ALOGV("Running %s in=%s out=%s\n", DEX2OAT_BIN, relative_input_file_name, output_file_name);
const char* argv[9 // program name, mandatory arguments and the final NULL
+ (have_dex2oat_isa_variant ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_isa_features ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_Xms_flag ? 2 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_Xmx_flag ? 2 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_compiler_filter_flag ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_threads_flag ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_swap_fd ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_image_fd ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_relocation_skip_flag ? 2 : 0)
+ (generate_debug_info ? 1 : 0)
+ (debuggable ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_app_image_format ? 1 : 0)
+ dex2oat_flags_count
+ (profile_fd == -1 ? 0 : 1)
+ (class_loader_context != nullptr ? 1 : 0)
+ (has_base_dir ? 1 : 0)
+ (have_dex2oat_large_app_threshold ? 1 : 0)];
int i = 0;
argv[i++] = DEX2OAT_BIN;
argv[i++] = zip_fd_arg;
argv[i++] = zip_location_arg;
argv[i++] = input_vdex_fd_arg;
argv[i++] = output_vdex_fd_arg;
argv[i++] = oat_fd_arg;
argv[i++] = oat_location_arg;
argv[i++] = instruction_set_arg;
if (have_dex2oat_isa_variant) {
argv[i++] = instruction_set_variant_arg;
}
if (have_dex2oat_isa_features) {
argv[i++] = instruction_set_features_arg;
}
if (have_dex2oat_Xms_flag) {
argv[i++] = RUNTIME_ARG;
argv[i++] = dex2oat_Xms_arg;
}
if (have_dex2oat_Xmx_flag) {
argv[i++] = RUNTIME_ARG;
argv[i++] = dex2oat_Xmx_arg;
}
if (have_dex2oat_compiler_filter_flag) {
argv[i++] = dex2oat_compiler_filter_arg;
}
if (have_dex2oat_threads_flag) {
argv[i++] = dex2oat_threads_arg;
}
if (have_dex2oat_swap_fd) {
argv[i++] = dex2oat_swap_fd;
}
if (have_dex2oat_image_fd) {
argv[i++] = dex2oat_image_fd;
}
if (generate_debug_info) {
argv[i++] = "--generate-debug-info";
}
if (debuggable) {
argv[i++] = "--debuggable";
}
if (have_app_image_format) {
argv[i++] = image_format_arg;
}
if (have_dex2oat_large_app_threshold) {
argv[i++] = dex2oat_large_app_threshold_arg;
}
if (dex2oat_flags_count) {
i += split(dex2oat_flags, argv + i);
}
if (have_dex2oat_relocation_skip_flag) {
argv[i++] = RUNTIME_ARG;
argv[i++] = dex2oat_norelocation;
}
if (profile_fd != -1) {
argv[i++] = profile_arg;
}
if (has_base_dir) {
argv[i++] = base_dir;
}
if (class_loader_context != nullptr) {
argv[i++] = class_loader_context_arg;
}
// Do not add after dex2oat_flags, they should override others for debugging.
argv[i] = NULL;
execv(DEX2OAT_BIN, (char * const *)argv);
ALOGE("execv(%s) failed: %s\n", DEX2OAT_BIN, strerror(errno));
}
其中,参数zip_fd和oat_fd都是打开文件描述符,指向的分别是正在安装的APK文件和要生成的OAT文件。OAT文件的生成过程主要就是涉及到将包含在APK里面的classes.dex文件的DEX字节码翻译成本地机器指令。这相当于是编写一个输入文件为DEX、输出文件为OAT的编译器
当我们选择了ART运行时时,Zygote进程在启动的过程中,会调用libart.so里面的函数JNI_CreateJavaVM来创建一个ART
/Volumes/aosp/android-8.1.0_r52/art/runtime/java_vm_ext.cc
extern "C" jint JNI_CreateJavaVM(JavaVM** p_vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* vm_args) {
ScopedTrace trace(__FUNCTION__);
const JavaVMInitArgs* args = static_cast(vm_args);
if (JavaVMExt::IsBadJniVersion(args->version)) {
LOG(ERROR) nOptions; ++i) {
JavaVMOption* option = &args->options[i];
options.push_back(std::make_pair(std::string(option->optionString), option->extraInfo));
}
bool ignore_unrecognized = args->ignoreUnrecognized;
if (!Runtime::Create(options, ignore_unrecognized)) {
return JNI_ERR;
}
// Initialize native loader. This step makes sure we have
// everything set up before we start using JNI.
android::InitializeNativeLoader();
Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();
bool started = runtime->Start();
if (!started) {
delete Thread::Current()->GetJniEnv();
delete runtime->GetJavaVM();
LOG(WARNING) GetJniEnv();
*p_vm = runtime->GetJavaVM();
return JNI_OK;
}
参数vm_args用作ART虚拟机的启动参数,它被转换为一个JavaVMInitArgs对象后,再按照Key-Value的组织形式保存一个Options向量中,并且以该向量作为参数传递给Runtime类的静态成员函数Create。
Runtime类的静态成员函数Create负责在进程中创建一个ART虚拟机。创建成功后,就调用Runtime类的另外一个静态成员函数Start启动该ART虚拟机。注意,这个创建ART虚拟的动作只会在Zygote进程中执行,SystemServer系统进程以及Android应用程序进程的ART虚拟机都是直接从Zygote进程fork出来共享的。这与Dalvik虚拟机的创建方式是完全一样的。
接下来我们就重点分析Runtime类的静态成员函数Create,它的实现如下所示
/Volumes/aosp/android-8.1.0_r52/art/runtime/runtime.cc
bool Runtime::Create(RuntimeArgumentMap&& runtime_options) {
// TODO: acquire a static mutex on Runtime to avoid racing.
if (Runtime::instance_ != nullptr) {
return false;
}
instance_ = new Runtime;
Locks::SetClientCallback(IsSafeToCallAbort);
if (!instance_->Init(std::move(runtime_options))) {
// TODO: Currently deleting the instance will abort the runtime on destruction. Now This will
// leak memory, instead. Fix the destructor. b/19100793.
// delete instance_;
instance_ = nullptr;
return false;
}
return true;
}
instance_是Runtime类的静态成员变量,它指向进程中的一个Runtime单例。这个Runtime单例描述的就是当前进程的ART虚拟机实例。
函数首先判断当前进程是否已经创建有一个ART虚拟机实例了。如果有的话,函数就立即返回。否则的话,就创建一个ART虚拟机实例,并且保存在Runtime类的静态成员变量instance_中,最后调用Runtime类的成员函数Init对该新创建的ART虚拟机进行初始化。
Runtime类的成员函数Init的实现如下所示:
bool Runtime::Init(RuntimeArgumentMap&& runtime_options_in) {
// (b/30160149): protect subprocesses from modifications to LD_LIBRARY_PATH, etc.
// Take a snapshot of the environment at the time the runtime was created, for use by Exec, etc.
env_snapshot_.TakeSnapshot();
RuntimeArgumentMap runtime_options(std::move(runtime_options_in));
ScopedTrace trace(__FUNCTION__);
CHECK_EQ(sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE), kPageSize);
MemMap::Init();
// Try to reserve a dedicated fault page. This is allocated for clobbered registers and sentinels.
// If we cannot reserve it, log a warning.
// Note: We allocate this first to have a good chance of grabbing the page. The address (0xebad..)
// is out-of-the-way enough that it should not collide with boot image mapping.
// Note: Don't request an error message. That will lead to a maps dump in the case of failure,
// leading to logspam.
{
constexpr uintptr_t kSentinelAddr =
RoundDown(static_cast(Context::kBadGprBase), kPageSize);
protected_fault_page_.reset(MemMap::MapAnonymous("Sentinel fault page",
reinterpret_cast(kSentinelAddr),
kPageSize,
PROT_NONE,
/* low_4g */ true,
/* reuse */ false,
/* error_msg */ nullptr));
if (protected_fault_page_ == nullptr) {
LOG(WARNING) Begin()) != kSentinelAddr) {
LOG(WARNING) HasBootImageSpace() && !allow_dex_file_fallback_) {
LOG(ERROR) AddThreadLifecycleCallback(Dbg::GetThreadLifecycleCallback());
callbacks_->AddClassLoadCallback(Dbg::GetClassLoadCallback());
jit_options_.reset(jit::JitOptions::CreateFromRuntimeArguments(runtime_options));
if (IsAotCompiler()) {
// If we are already the compiler at this point, we must be dex2oat. Don't create the jit in
// this case.
// If runtime_options doesn't have UseJIT set to true then CreateFromRuntimeArguments returns
// null and we don't create the jit.
jit_options_->SetUseJitCompilation(false);
jit_options_->SetSaveProfilingInfo(false);
}
// Use MemMap arena pool for jit, malloc otherwise. Malloc arenas are faster to allocate but
// can't be trimmed as easily.
const bool use_malloc = IsAotCompiler();
arena_pool_.reset(new ArenaPool(use_malloc, /* low_4gb */ false));
jit_arena_pool_.reset(
new ArenaPool(/* use_malloc */ false, /* low_4gb */ false, "CompilerMetadata"));
if (IsAotCompiler() && Is64BitInstructionSet(kRuntimeISA)) {
// 4gb, no malloc. Explanation in header.
low_4gb_arena_pool_.reset(new ArenaPool(/* use_malloc */ false, /* low_4gb */ true));
}
linear_alloc_.reset(CreateLinearAlloc());
BlockSignals();
InitPlatformSignalHandlers();
// Change the implicit checks flags based on runtime architecture.
switch (kRuntimeISA) {
case kArm:
case kThumb2:
case kX86:
case kArm64:
case kX86_64:
case kMips:
case kMips64:
implicit_null_checks_ = true;
// Installing stack protection does not play well with valgrind.
implicit_so_checks_ = !(RUNNING_ON_MEMORY_TOOL && kMemoryToolIsValgrind);
break;
default:
// Keep the defaults.
break;
}
if (!no_sig_chain_) {
// Dex2Oat's Runtime does not need the signal chain or the fault handler.
if (implicit_null_checks_ || implicit_so_checks_ || implicit_suspend_checks_) {
fault_manager.Init();
// These need to be in a specific order. The null point check handler must be
// after the suspend check and stack overflow check handlers.
//
// Note: the instances attach themselves to the fault manager and are handled by it. The manager
// will delete the instance on Shutdown().
if (implicit_suspend_checks_) {
new SuspensionHandler(&fault_manager);
}
if (implicit_so_checks_) {
new StackOverflowHandler(&fault_manager);
}
if (implicit_null_checks_) {
new NullPointerHandler(&fault_manager);
}
if (kEnableJavaStackTraceHandler) {
new JavaStackTraceHandler(&fault_manager);
}
}
}
std::string error_msg;
java_vm_ = JavaVMExt::Create(this, runtime_options, &error_msg);
if (java_vm_.get() == nullptr) {
LOG(ERROR) GetThreadId(), ThreadList::kMainThreadId);
CHECK(self != nullptr);
self->SetCanCallIntoJava(!IsAotCompiler());
// Set us to runnable so tools using a runtime can allocate and GC by default
self->TransitionFromSuspendedToRunnable();
// Now we're attached, we can take the heap locks and validate the heap.
GetHeap()->EnableObjectValidation();
CHECK_GE(GetHeap()->GetContinuousSpaces().size(), 1U);
if (UNLIKELY(IsAotCompiler())) {
class_linker_ = new AotClassLinker(intern_table_);
} else {
class_linker_ = new ClassLinker(intern_table_);
}
if (GetHeap()->HasBootImageSpace()) {
bool result = class_linker_->InitFromBootImage(&error_msg);
if (!result) {
LOG(ERROR) VerifyImageAllocations();
}
}
if (boot_class_path_string_.empty()) {
// The bootclasspath is not explicitly specified: construct it from the loaded dex files.
const std::vector& boot_class_path = GetClassLinker()->GetBootClassPath();
std::vector dex_locations;
dex_locations.reserve(boot_class_path.size());
for (const DexFile* dex_file : boot_class_path) {
dex_locations.push_back(dex_file->GetLocation());
}
boot_class_path_string_ = android::base::Join(dex_locations, ':');
}
{
ScopedTrace trace2("AddImageStringsToTable");
GetInternTable()->AddImagesStringsToTable(heap_->GetBootImageSpaces());
}
if (IsJavaDebuggable()) {
// Now that we have loaded the boot image, deoptimize its methods if we are running
// debuggable, as the code may have been compiled non-debuggable.
DeoptimizeBootImage();
}
} else {
std::vector dex_filenames;
Split(boot_class_path_string_, ':', &dex_filenames);
std::vector dex_locations;
if (!runtime_options.Exists(Opt::BootClassPathLocations)) {
dex_locations = dex_filenames;
} else {
dex_locations = runtime_options.GetOrDefault(Opt::BootClassPathLocations);
CHECK_EQ(dex_filenames.size(), dex_locations.size());
}
std::vector boot_class_path;
if (runtime_options.Exists(Opt::BootClassPathDexList)) {
boot_class_path.swap(*runtime_options.GetOrDefault(Opt::BootClassPathDexList));
} else {
OpenDexFiles(dex_filenames,
dex_locations,
runtime_options.GetOrDefault(Opt::Image),
&boot_class_path);
}
instruction_set_ = runtime_options.GetOrDefault(Opt::ImageInstructionSet);
if (!class_linker_->InitWithoutImage(std::move(boot_class_path), &error_msg)) {
LOG(ERROR) trace_file_size = runtime_options.ReleaseOrDefault(Opt::MethodTraceFileSize);
trace_config_->trace_mode = Trace::TraceMode::kMethodTracing;
trace_config_->trace_output_mode = runtime_options.Exists(Opt::MethodTraceStreaming) ?
Trace::TraceOutputMode::kStreaming :
Trace::TraceOutputMode::kFile;
}
// TODO: move this to just be an Trace::Start argument
Trace::SetDefaultClockSource(runtime_options.GetOrDefault(Opt::ProfileClock));
// Pre-allocate an OutOfMemoryError for the double-OOME case.
self->ThrowNewException("Ljava/lang/OutOfMemoryError;",
"OutOfMemoryError thrown while trying to throw OutOfMemoryError; "
"no stack trace available");
pre_allocated_OutOfMemoryError_ = GcRoot....
......}
创建好ART虚拟机堆后,Runtime类的成员函数Init接着又创建了一个JavaVMExt实例。这个JavaVMExt实例最终是要返回给调用者的,使得调用者可以通过该JavaVMExt实例来和ART虚拟机交互。再接下来,Runtime类的成员函数Init通过Thread类的成员函数Attach将当前线程作为ART虚拟机的主线程,使得当前线程可以调用ART虚拟机提供的JNI接口
Runtime类的成员函数GetHeap返回的便是当前ART虚拟机的堆,也就是前面创建的ART虚拟机堆。通过调用Heap类的成员函数GetContinuousSpaces可以获得堆里面的连续空间列表。如果这个列表的第一个连续空间是一个Image空间,那么就调用ClassLinker类的静态成员函数CreateFromImage来创建一个ClassLinker对象。否则的话,上述ClassLinker对象就要通过ClassLinker类的另外一个静态成员函数CreateFromCompiler来创建。创建出来的ClassLinker对象是后面ART虚拟机加载加载Java类时要用到的。
后面我们分析ART虚拟机的垃圾收集机制时会看到,ART虚拟机的堆包含有三个连续空间和一个不连续空间。三个连续空间分别用来分配不同的对象。当第一个连续空间不是Image空间时,就表明当前进程不是Zygote进程,而是安装应用程序时启动的一个dex2oat进程。安装应用程序时启动的dex2oat进程也会在内部创建一个ART虚拟机,不过这个ART虚拟机是用来将DEX字节码编译成本地机器指令的,而Zygote进程创建的ART虚拟机是用来运行应用程序的。
接下来我们主要分析ParsedOptions类的静态成员函数Create和ART虚拟机堆Heap的构造函数,以便可以了解ART虚拟机的启动参数解析过程和ART虚拟机的堆创建过程。
Heap类的构造函数的