Knife4j和Swagger3注解使用与SpringBoot各种参数校验
Knife4j和Swagger3注解使用与SpringBoot各种参数校验
Knife4j和Swagger3注解使用与SpringBoot各种参数校验博客地址
1、Knife4j和Swagger3注解使用
1、Knife4j是什么
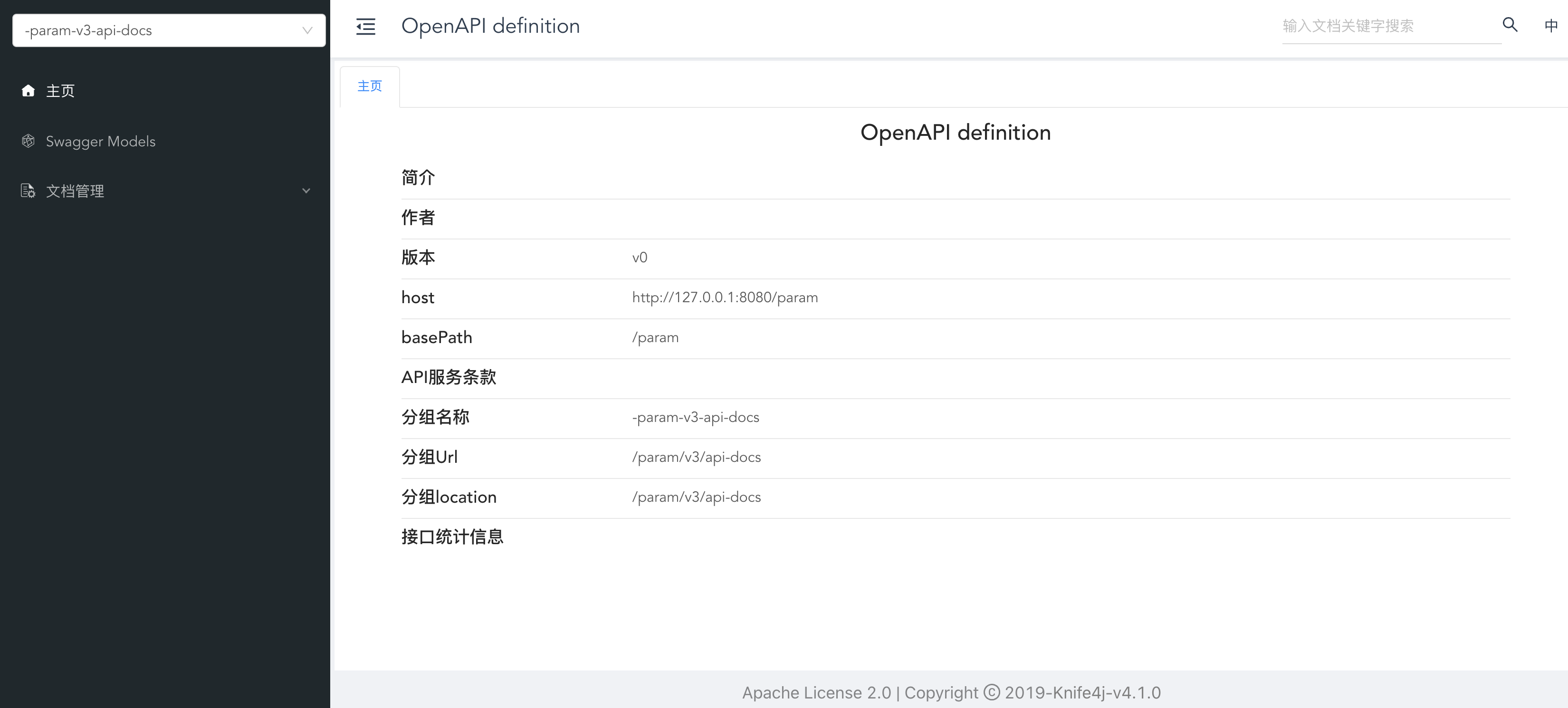
Knife4j是一个集Swagger3 和 OpenAPI3 为一体的增强解决方案
2、pom.xml
spring-boot-param-validation
4.0.0
com.xx
spring-boot-param-validation
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
3.0.8
17
17
UTF-8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
com.github.xiaoymin
knife4j-openapi3-jakarta-spring-boot-starter
4.4.0
cn.hutool
hutool-all
5.8.19
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
3、application.yml
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /param
4、启动类
package com.xx;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import java.net.InetAddress;
/**
* @Author: xueqimiao
* @Date: 2024/3/4 09:11
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class PramValidationApplication {
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args){
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext application = SpringApplication.run(PramValidationApplication.class, args);
stopWatch.stop();
Environment env = application.getEnvironment();
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
String port = env.getProperty("server.port");
String path = env.getProperty("server.servlet.context-path");
log.info("\n--------------------------------------------------------\n\t" +
"Application Manager is running! Access URLs:\n\t" +
"Local: \t\thttp://127.0.0.1:" + port + path + "/\n\t" +
"External: \thttp://" + ip + ":" + port + path + "/\n\t" +
"Swagger文档: \thttp://" + ip + ":" + port + path + "/doc.html\n\t" +
"服务启动完成,耗时: \t" + stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds() + "S\n" +
"----------------------------------------------------------");
}
}
使用 @SneakyThrows 注解时,需要注意以下几点:
@SneakyThrows 注解只能用于方法上,不能用于字段、构造函数等其他地方。
方法上使用了 @SneakyThrows 注解后,编译器会忽略该方法中的受检查异常,并自动生成异常抛出的代码。
使用 @SneakyThrow注解时要谨慎,确保在方法中的异常处理逻辑充分而且合理。因为异常被转换为运行时异常,可能会隐藏原始的异常信息,增加调试的难度。
@SneakyThrows 注解可以配合使用多个异常类型,比如 @SneakyThrows({IOException.class,
InterruptedException.class})。
需要注意的是,Lombok 是一个Java库,用于通过注解自动消除样板代码。它可以减少代码量,提高开发效率,但在使用之前,请确保已经熟悉并理解所使用的注解的作用和影响。
5、修改主界面信息
package com.xx.config;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.OpenAPI;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.Info;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.License;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author: xueqimiao
* @Date: 2024/3/4 09:33
*/
@Configuration
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.info(new Info()
.title("小薛博客官方文档")
.version("1.0")
.description( "`我是小薛博客官方文档`,**你知道吗**")
.termsOfService("https://blog.xueqimiao.com/")
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0")
.url("https://blog.xueqimiao.com/")));
}
}
修改扫包:
springdoc:
group-configs:
- group: 'xx'
paths-to-match: '/**'
# 生成文档所需的扫包路径,一般为启动类目录 可以不配置 会自动识别
packages-to-scan: com.xx.controller
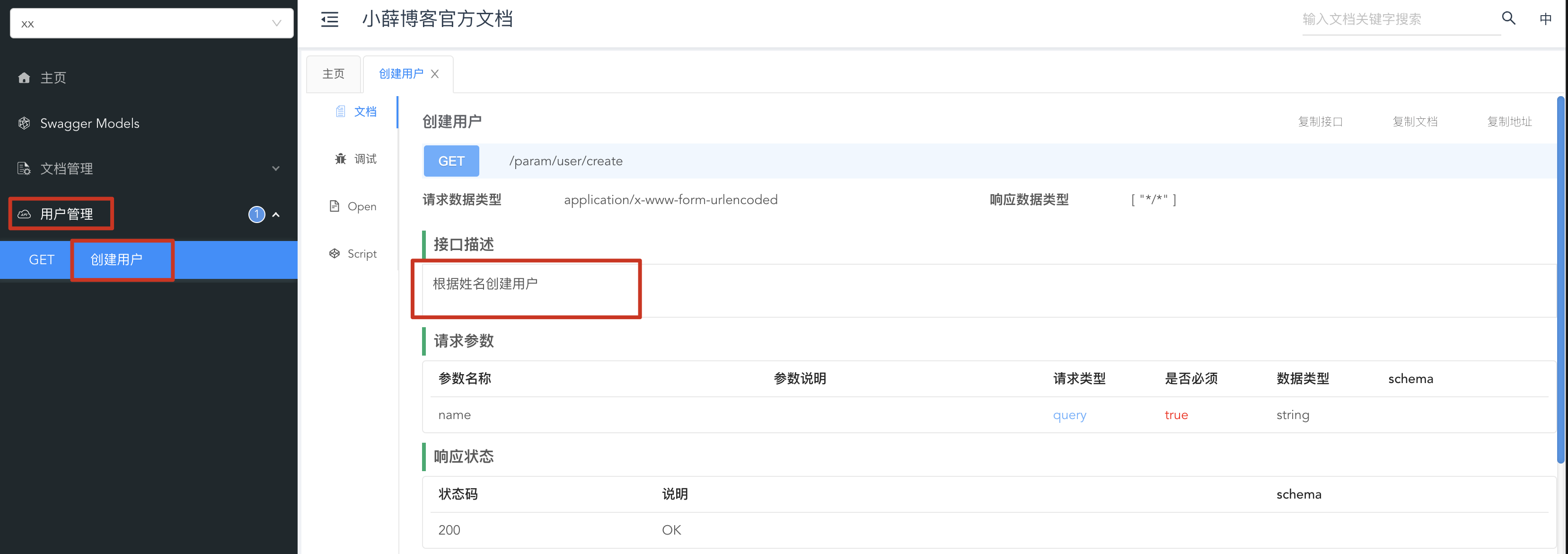
6、@Tag与@Operation
package com.xx.controller;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: xueqimiao
* @Date: 2024/3/4 09:13
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Tag(name = "用户管理")
public class UserController {
@Operation(summary = "创建用户",description = "根据姓名创建用户")
@GetMapping("/create")
public ResponseEntity create(String name){
return ResponseEntity.ok(name);
}
}
7、@Schema
package com.xx.dto;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.media.Schema;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @Author: xueqimiao
* @Date: 2024/3/4 09:13
*/
@Data
public class UserDTO implements Serializable {
@Schema(title = "userId", description = "主键id", defaultValue = "1")
private String id;
@Schema(description = "名称", defaultValue = "张飞")
private String name;
@Schema(description = "年龄", defaultValue = "18", hidden = true)
private String age;
}
@Schema(description = "状态", allowableValues = {"Y", "N"})
private String validStatus;

@Operation(summary = "创建用户-createOne",description = "根据姓名创建用户1")
@PostMapping("/createOne")
public ResponseEntity createOne(@RequestBody UserDTO user){
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}
8、@Parameter
@Operation(summary = "获取用户信息", description = "根据id获取用户信息")
@PostMapping("/getUserById")
@Parameter(name = "id", description = "用户id", in = ParameterIn.QUERY, required = true, example = "6")
public ResponseEntity getUserById(String id) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(id);
}
@Operation(summary = "获取用户信息", description = "根据姓名、年龄获取用户信息")
@PostMapping("/getUserByNameAndAge")
@Parameters({
@Parameter(name = "id", description = "用户id", in = ParameterIn.QUERY, required = true, example = "6"),
@Parameter(name = "name", description = "用户姓名", in = ParameterIn.QUERY, required = true, example = "00")
})
public ResponseEntity getUserByNameAndAge(String id, String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(id);
}
9、接口添加作者
需要通过配置yml配置文件开启增强功能
knife4j: enable: true
接口上:
@ApiOperationSupport(author = "xx")
@Operation(summary = "创建用户", description = "根据姓名创建用户")
@GetMapping("/create")
public ResponseEntity create(String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(name);
}
Controller上:
@ApiSupport(author = "xxxx")
所代表的意思是该Controller模块下所有的接口都是该作者负责开发,当然用@ApiOperationSupport的注解也能覆盖
10、生产环境关闭文档
knife4j: enable: true # 开启生产环境屏蔽 production: true
11、Basic认证功能
knife4j:
enable: true
# 开启生产环境屏蔽
# production: true
# 开启Swagger的Basic认证功能,默认是false
basic:
enable: true
# Basic认证用户名
username: test
# Basic认证密码
password: 123
12、接口排序
排序规则是使用Knife4j提供的增强注解@ApiOperationSupport中的order字段
package com.xx.controller;
import com.github.xiaoymin.knife4j.annotations.ApiOperationSupport;
import com.github.xiaoymin.knife4j.annotations.ApiSupport;
import com.xx.dto.UserDTO;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameters;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.enums.ParameterIn;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* @Author: xueqimiao
* @Date: 2024/3/4 09:13
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Tag(name = "用户管理")
@ApiSupport(author = "xxxx")
public class UserController {
@ApiOperationSupport(author = "xx",order = 1)
@Operation(summary = "创建用户", description = "根据姓名创建用户")
@GetMapping("/create")
public ResponseEntity create(String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(name);
}
@ApiOperationSupport(author = "xx",order = 2)
@Operation(summary = "创建用户-createOne", description = "根据姓名创建用户1")
@PostMapping("/createOne")
public ResponseEntity createOne(@RequestBody UserDTO user) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}
@ApiOperationSupport(author = "xx",order = 3)
@Operation(summary = "获取用户信息", description = "根据id获取用户信息")
@PostMapping("/getUserById")
@Parameter(name = "id", description = "用户id", in = ParameterIn.QUERY, required = true, example = "6")
public ResponseEntity getUserById(String id) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(id);
}
@ApiOperationSupport(author = "xx",order = 4)
@Operation(summary = "获取用户信息", description = "根据姓名、年龄获取用户信息")
@PostMapping("/getUserByNameAndAge")
@Parameters({
@Parameter(name = "id", description = "用户id", in = ParameterIn.QUERY, required = true, example = "6"),
@Parameter(name = "name", description = "用户姓名", in = ParameterIn.QUERY, required = true, example = "00")
})
public ResponseEntity getUserByNameAndAge(String id, String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(id);
}
}
2、SpringBoot参数校验
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-validation
com.xx
xx-common-core
1.4.0
1、非空校验
@NotNull(message = "用户id不能为空") private String id; @NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空") private String name; @NotEmpty(message = "houseIds不能为空") private List houseIds;
@Operation(summary = "创建用户-createOne", description = "根据姓名创建用户1")
@PostMapping("/createOne")
public ResponseEntity createOne(@RequestBody @Validated UserDTO user) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}
@NotNull: 它用于标记一个属性或方法参数不能为空。它适用于任何类型的参数,包括字符串、集合、数组等。如果一个参数被标记为 @NotNull,在校验过程中,如果该参数的值为 null,将会触发校验失败,并返回相应的错误信息。
@NotBlank: 它用于标记一个字符串类型的属性或方法参数不能为空,并且不能只包含空格。它会先对参数进行 @NotNull 的非空校验,然后再对字符串进行额外的校验。如果参数的值为 null 或者只包含空格,将会触发校验失败,并返回相应的错误信息。
@NotEmpty:用于限制集合、数组、Map 等类型属性值不能为 null 或空。
JSR-303 是 Java Specification Request 303 的缩写,它定义了 Java 中用于对象校验的标准规范,即 Bean Validation 规范。
JSR-380 是 Java Specification Request 380 的缩写,它是 JSR-303 规范的升级版,也被称为 Bean Validation 2.0 规范。
2、自定义异常
https://blog.xueqimiao.com/springboot/869828/
package com.xx.handler;
import com.xx.common.Result;
import com.xx.common.ResultCodeEnum;
import com.xx.utils.FunctionUtils;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author: xueqimiao
* @Date: 2024/3/4 11:31
*/
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 集中处理参数丢失、缺少参数、参数为空 情况异常
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result methodArgumentNotValidException(HttpServletRequest request, MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
BindingResult bindingResult = ex.getBindingResult();
List fieldErrors = bindingResult.getFieldErrors();
List messageMap = FunctionUtils.map(fieldErrors, FieldError::getDefaultMessage);
// 逗号拼接
String message = String.join(",", messageMap);
return Result.error(ResultCodeEnum.PARAM_VERIFICATION_FAIL.getCode(), message);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Result handleException(Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return Result.error("操作失败," + e.getMessage());
}
}
3、长度校验
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空") @Length(min = 2, max = 10, message = "用户名长度必须在2-10之间") private String name;
4、范围校验
// 数字 @Min(value = 1, message = "年龄不能小于1") @Max(value = 100, message = "年龄不能大于100") private Integer age; @Range(min = 1, max = 100, message = "年龄2必须在1到100之间") private Integer age2;
// 金额 @NotNull(message = "金额不能为空") @DecimalMin(value = "0.01", message = "金额不能小于0.01") @DecimalMax(value = "10.00", message = "金额不能大于10.00") private BigDecimal amount;
// 集合 @Size(min = 1, max = 3, message = "houseIds长度必须在1-3之间") private List houseIds;
// 日期 @Future(message = "日期必须是未来的日期") private Date futureDate; @Past(message = "日期必须是过去的日期") private Date pastDate;
5、拓展SpringBoot日期格式化
@JsonFormat(timezone = "GMT+8", pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") private Date futureDate; @JsonFormat(timezone = "GMT+8", pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") private Date pastDate;
6、正则校验
@Pattern(regexp = "^1\\d{10}$", message = "手机号格式不正确")
private String phone;
7、邮箱校验
@Email(message = "邮箱格式不正确") private String email;
8、RequestParam/PathVariable参数校验
添加全局异常
@ExceptionHandler(value = ConstraintViolationException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result constraintViolationException(HttpServletRequest request, ConstraintViolationException ex) {
Set[] groups() default {};
// 负载
Class[] groups() default {};
Class> enumClass();
// 枚举字段方法
String enumFieldMethod();
// 是否允许为空
boolean allowNull() default false;
// 分组
Class[] groups() default {};
// 负载
Class> enumClass;
private Method enumFieldMethod;
private boolean allowNull;
@Override
public void initialize(EnumFieldValid constraintAnnotation) {
enumClass = constraintAnnotation.enumClass();
allowNull = constraintAnnotation.allowNull();
try {
enumFieldMethod = enumClass.getMethod(constraintAnnotation.enumFieldMethod());
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("指定的枚举字段方法不存在", e);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(Object value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if (value == null) {
return allowNull; // 允许空值时返回 true,不允许时返回 false
}
try {
for (Enum enumConstant : enumClass.getEnumConstants()) {
Object enumFieldValue = enumFieldMethod.invoke(enumConstant);
// Debug information
System.out.println("Comparing value: " + value + " with enum field value: " + enumFieldValue);
if (enumFieldValue != null && String.valueOf(enumFieldValue).equals(value)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("枚举验证过程中发生错误", e);
}
}
}
@EnumFieldValid(enumClass = StatusEnum.class, enumFieldMethod = "getCode", message = "状态码必须为1或2")
@Schema(description = "状态", allowableValues = {"1", "2"})
private String validStatus;
14、@Valid和@Validated区别
| 区别 | @Valid | @Validated |
|---|---|---|
| 提供者 | JSR-303规范 | Spring |
| 是否支持分组 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 嵌套校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
写在最后
好了,今天关于技术探索、学习和项目难点的分享就到这里啦!我知道,很多小伙伴在技术的道路上可能会遇到各种各样的问题,有时候会觉得迷茫,有时候会想要放弃。但是我想说,别灰心,别气馁!
咱们都是从不会到会,从做不好到能做好的。就像爬山一样,有时候会觉得路途艰辛,气喘吁吁,但只要一步一个脚印地往上走,最终一定能登上山顶,看到那美丽的风景。
所以啊,不管是学习新技术,还是做个人项目,只要咱们保持那股子热情和劲头,遇到问题多琢磨琢磨,多尝试尝试,总会把问题解决的。相信自己,你就是那个未来的技术大佬!加油吧!