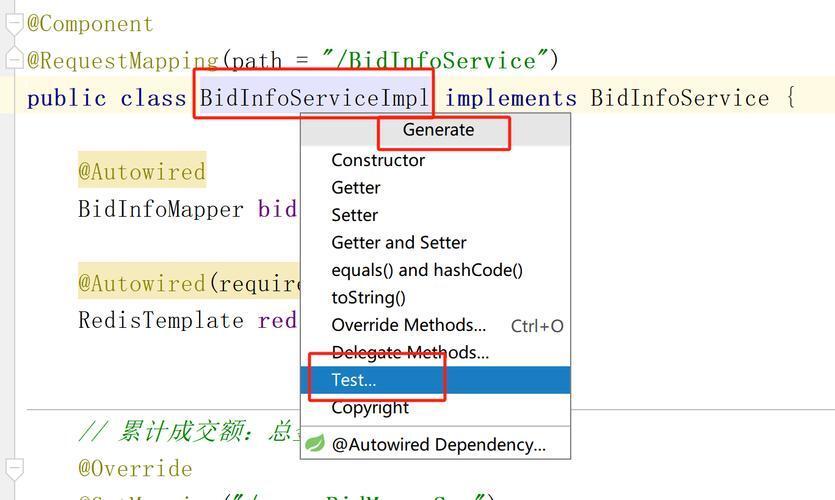
Spring Boot 单元测试使用教程(仅供参考)
单元测试是软件开发中至关重要的一环,Spring Boot 提供了强大的测试支持。以下是 Spring Boot 单元测试的详细教程。
1. 准备工作
1.1 添加测试依赖
在 pom.xml 中添加测试相关依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework
spring-test
test
org.assertj
assertj-core
3.24.2
test
1.2 测试类基本结构
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class MyApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
// 测试Spring上下文是否正常加载
}
}
2. 不同类型的测试
2.1 服务层测试
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.mockito.InjectMocks;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.junit.jupiter.MockitoExtension;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class UserServiceTest {
@Mock
private UserRepository userRepository;
@InjectMocks
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testGetUserById() {
// 准备测试数据
User mockUser = new User(1L, "test@example.com", "Test User");
// 定义mock行为
when(userRepository.findById(1L)).thenReturn(Optional.of(mockUser));
// 调用测试方法
User result = userService.getUserById(1L);
// 验证结果
assertEquals("Test User", result.getName());
verify(userRepository, times(1)).findById(1L);
}
}
2.2 控制器层测试
使用MockMvc
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.*;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class UserControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void testGetUser() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/api/users/1"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.name").value("Test User"));
}
}
使用WebTestClient (WebFlux)
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.reactive.AutoConfigureWebTestClient;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.reactive.server.WebTestClient;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureWebTestClient
public class UserControllerWebTestClientTest {
@Autowired
private WebTestClient webTestClient;
@Test
public void testGetUser() {
webTestClient.get().uri("/api/users/1")
.exchange()
.expectStatus().isOk()
.expectBody()
.jsonPath("$.name").isEqualTo("Test User");
}
}
2.3 数据库测试
使用@DataJpaTest
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.TestEntityManager;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
@DataJpaTest
public class UserRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private TestEntityManager entityManager;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
public void testFindByEmail() {
// 准备测试数据
User user = new User("test@example.com", "Test User");
entityManager.persist(user);
entityManager.flush();
// 调用测试方法
User found = userRepository.findByEmail(user.getEmail());
// 验证结果
assertThat(found.getEmail()).isEqualTo(user.getEmail());
}
}
使用@SpringBootTest + 测试数据库
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
@ActiveProfiles("test")
@Transactional
public class UserServiceIntegrationTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
public void testCreateUser() {
User newUser = new User("new@example.com", "New User");
User savedUser = userService.createUser(newUser);
assertNotNull(savedUser.getId());
assertEquals("New User", savedUser.getName());
User found = userRepository.findById(savedUser.getId()).orElse(null);
assertEquals("New User", found.getName());
}
}
3. 常用测试技巧
3.1 参数化测试
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ValueSource;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
public class ParameterizedTests {
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = {"racecar", "radar", "madam"})
public void testPalindromes(String candidate) {
assertTrue(StringUtils.isPalindrome(candidate));
}
}
3.2 测试异常
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows;
public class ExceptionTest {
@Test
public void testException() {
UserService userService = new UserService();
assertThrows(UserNotFoundException.class, () -> {
userService.getUserById(999L);
});
}
}
3.3 测试私有方法
虽然不推荐直接测试私有方法,但有时确实需要:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class PrivateMethodTest {
@Test
public void testPrivateMethod() throws Exception {
MyService service = new MyService();
Method method = MyService.class.getDeclaredMethod("privateMethod", String.class);
method.setAccessible(true);
String result = (String) method.invoke(service, "input");
assertEquals("expected", result);
}
}
4. 测试配置
4.1 使用测试配置文件
创建 src/test/resources/application-test.properties:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password= spring.h2.console.enabled=true
然后在测试类上使用:
@ActiveProfiles("test")
4.2 使用测试切片
Spring Boot 提供了多种测试切片注解:
-
@WebMvcTest - 只测试MVC层
-
@DataJpaTest - 只测试JPA组件
-
@JsonTest - 只测试JSON序列化
-
@RestClientTest - 只测试REST客户端
@WebMvcTest(UserController.class) public class UserControllerSliceTest { @Autowired private MockMvc mockMvc; @MockBean private UserService userService; @Test public void testGetUser() throws Exception { when(userService.getUserById(1L)).thenReturn(new User(1L, "test@example.com", "Test User")); mockMvc.perform(get("/api/users/1")) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.name").value("Test User")); } }5. 测试最佳实践
-
命名规范:测试方法名应清晰表达测试意图,如 shouldReturnUserWhenValidIdProvided()
-
单一职责:每个测试方法只测试一个功能点
-
AAA模式:遵循Arrange-Act-Assert模式组织测试代码
-
避免依赖:测试之间不应有依赖关系
-
快速反馈:保持测试快速执行,避免I/O操作
(图片来源网络,侵删) -
覆盖率:追求合理的测试覆盖率,但不要盲目追求100%
-
Mock适度:不要过度使用mock,集成测试也很重要
(图片来源网络,侵删)
6. 高级主题
6.1 自定义测试注解
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles; import java.lang.annotation.*; @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @SpringBootTest @ActiveProfiles("test") public @interface MyIntegrationTest { }然后可以在测试类上使用 @MyIntegrationTest 替代多个注解。
6.2 测试容器支持
使用Testcontainers进行集成测试:
(图片来源网络,侵删)import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.testcontainers.containers.PostgreSQLContainer; import org.testcontainers.junit.jupiter.Container; import org.testcontainers.junit.jupiter.Testcontainers; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @Testcontainers @SpringBootTest public class UserRepositoryTestContainersTest { @Container public static PostgreSQLContainer postgreSQLContainer = new PostgreSQLContainer("postgres:13") .withDatabaseName("testdb") .withUsername("test") .withPassword("test"); @Test public void testWithRealDatabase() { // 测试代码 } }6.3 测试Spring Security
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithMockUser; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.*; @SpringBootTest @AutoConfigureMockMvc public class SecuredControllerTest { @Autowired private MockMvc mockMvc; @Test @WithMockUser(username="admin", roles={"ADMIN"}) public void testAdminEndpoint() throws Exception { mockMvc.perform(get("/api/admin")) .andExpect(status().isOk()); } @Test @WithMockUser(username="user", roles={"USER"}) public void testAdminEndpointForbidden() throws Exception { mockMvc.perform(get("/api/admin")) .andExpect(status().isForbidden()); } }7. 总结
Spring Boot 提供了全面的测试支持,从单元测试到集成测试,从Mock测试到真实环境测试。合理使用这些工具可以大大提高代码质量和开发效率。
记住测试金字塔原则:多写单元测试,适量集成测试,少量端到端测试。
-
免责声明:我们致力于保护作者版权,注重分享,被刊用文章因无法核实真实出处,未能及时与作者取得联系,或有版权异议的,请联系管理员,我们会立即处理! 部分文章是来自自研大数据AI进行生成,内容摘自(百度百科,百度知道,头条百科,中国民法典,刑法,牛津词典,新华词典,汉语词典,国家院校,科普平台)等数据,内容仅供学习参考,不准确地方联系删除处理! 图片声明:本站部分配图来自人工智能系统AI生成,觅知网授权图片,PxHere摄影无版权图库和百度,360,搜狗等多加搜索引擎自动关键词搜索配图,如有侵权的图片,请第一时间联系我们。