Function calling的过程
文章目录
- 逐段讲清 **LLM Function Calling(函数调用)** 的典型链路。
- 1. 角色与概念 | Actors & Concepts
- 2. 全流程时序 | End-to-End Sequence
- 3. 关键细节 | Key Implementation Notes
- 4. 最小可用示例(伪代码) | Minimal Example (Pseudo-Python)
- 5. 常见坑 / FAQ
- TL;DR
逐段讲清 LLM Function Calling(函数调用) 的典型链路。
1. 角色与概念 | Actors & Concepts
ZH:
- 开发者 (Developer):用 JSON-Schema 描述可调用函数。
- 用户 (User):提出自然语言请求。
- 模型 (LLM):在推理时决定是否调用函数、选哪一个、填什么参数。
- 执行器 (Caller / Tool Runtime):真正跑代码或访问外部 API,把结果回给模型。
EN –
- Developer supplies JSON-Schema definitions of callable functions.
- User sends a request in natural language.
- LLM decides whether, and how, to call a function.
- Caller / Tool Runtime executes the function and returns results to the model.
2. 全流程时序 | End-to-End Sequence
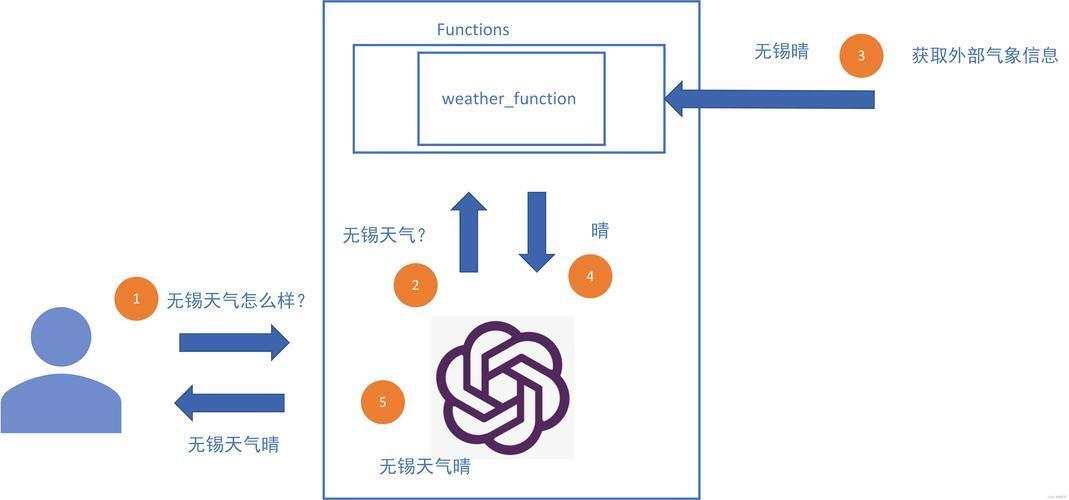
# 步骤 (ZH) Step (EN) 1 注册函数:开发者在 functions 字段传入 JSON-Schema,示例:
{"name":"weather","parameters":{"type":"object","properties":{"location":{"type":"string"}}}}Register functions via the functions array in the API call, giving JSON-Schema for each. 2 输入消息:messages=[{"role":"user","content":"今天天气如何?"}] User message is sent in messages. 3 模型推理:LLM 读取系统+用户信息,若判断需要函数→输出 role:"assistant", "name":"weather", "arguments":{...} Model reasoning: If it decides a function is needed, it emits a tool call with role:"assistant" and name, arguments. 4 执行器调用:客户端检测到 name 字段→调用本地或远程函数→得到返回值,如 {"temp":25} Caller executes detected function, obtains result JSON. 5 结果回注:把结果作为 role:"function", "name":"weather", "content":"{\"temp\":25}" 再塞进 messages Inject result back as a function role message so the model can see it. 6 模型二次生成:LLM 看到函数输出后,再生成最终自然语言回答。 Second pass: model crafts the final user-visible response, informed by result. 从开发者视角看,就是 “定义 → 监听 → 调用 → 回注” 四件事。
From the dev perspective: define → watch → call → inject.
3. 关键细节 | Key Implementation Notes
-
JSON-Schema 精度
- 字段类型、必选/可选决定模型填参质量。尽量用 enum, minimum, pattern 等约束减少幻觉。
- Use rich JSON-Schema constraints (enum, minimum, pattern) to steer the model toward valid args.
-
多轮调用
- 模型可串联多次函数:例如先 search_flights 再 book_flight。保持每轮都把结果作为 function role 回注即可。
- Chained calls work: keep injecting each result back as a function message.
-
流式 (Streaming)
- 在 OpenAI 流接口(stream=true)里,tool_calls δ块先到,客户端可即时触发执行。
- With streaming, tool-call deltas arrive early, enabling near-real-time actions.
-
错误处理
- 若执行失败,把错误描述同样作为 function 消息交给模型,让它决定重试/解释。
- Return errors as function role messages so the model can handle retries or apologies.
-
安全与权限
- 在执行器侧校验参数,避免模型注入恶意 shell 字符串。
- Validate args server-side; the JSON schema itself is not a security boundary.
4. 最小可用示例(伪代码) | Minimal Example (Pseudo-Python)
# 1. define schema functions = [{ "name": "weather", "description": "Get current weather", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}}, "required": ["location"] } }] # 2. first API call messages = [{"role":"user","content":"帮我查一下北京天气"}] resp = openai.ChatCompletion.create(model="gpt-4o", messages=messages, functions=functions) # 3. if resp.choices[0].finish_reason == "tool_call": tool_call = resp.choices[0].message args = json.loads(tool_call["arguments"]) result = get_weather(args["location"]) # 4. feed back messages += [ tool_call, {"role":"function","name":"weather","content":json.dumps(result)} ] final = openai.ChatCompletion.create(model="gpt-4o", messages=messages) print(final.choices[0].message["content"])5. 常见坑 / FAQ
问题 处理建议 模型拒绝填参数 检查 system prompt 是否允许工具;确保 schema 名称易懂;给示例调用。 参数格式错位 使用 json.loads() 校验;在 schema 里加 format, pattern。 连续调用失序 每轮都把 完整历史+最新函数结果发回;保持 deterministic。 TL;DR
- Function Calling = LLM decides + runtime executes + LLM finishes。
- 只需掌握 JSON-Schema 定义、工具消息注入、循环两轮,即可把“智能体”接入任意后端逻辑。
Master the pattern once and you can wire your Llama/GPT/Claude agent to databases, SaaS APIs, or even a coffee machine.
(图片来源网络,侵删)(图片来源网络,侵删)(图片来源网络,侵删)
-
- TL;DR
免责声明:我们致力于保护作者版权,注重分享,被刊用文章因无法核实真实出处,未能及时与作者取得联系,或有版权异议的,请联系管理员,我们会立即处理! 部分文章是来自自研大数据AI进行生成,内容摘自(百度百科,百度知道,头条百科,中国民法典,刑法,牛津词典,新华词典,汉语词典,国家院校,科普平台)等数据,内容仅供学习参考,不准确地方联系删除处理! 图片声明:本站部分配图来自人工智能系统AI生成,觅知网授权图片,PxHere摄影无版权图库和百度,360,搜狗等多加搜索引擎自动关键词搜索配图,如有侵权的图片,请第一时间联系我们。